In the digital age, the sanctity of personal privacy is more contested than ever, with tech giants constantly under scrutiny for how they handle user data. Apple, with its flagship iPhone, has positioned itself as a stalwart of privacy, promising users unparalleled protection of their personal information. This claim, amidst a landscape where data breaches and privacy violations are commonplace, offers a beacon of hope for many. Yet, the true measure of Apple’s iPhone privacy is not just in its marketing but in the intricate details of its policies, technologies, and the occasional controversies that challenge its privacy-first narrative.
Contents
The Foundation of iPhone’s Privacy
Apple has long touted privacy as a cornerstone of its user experience, integrating it deeply into the iOS ecosystem. The company’s privacy policy articulates a commitment to limit the collection of personal data, use it responsibly, and protect it with robust security measures. This commitment is reflected in features like end-to-end encryption in iMessage and FaceTime, ensuring that no one but the communicating parties can access the content of their conversations.
Moreover, iOS offers users granular control over app permissions, allowing them to decide precisely which data each app can access. Features like the App Tracking Transparency framework empower users to prevent apps from tracking their activity across other companies’ apps and websites. This proactive approach to privacy enables users to manage their digital footprint more effectively, setting a benchmark for privacy standards in the mobile industry.
CSAM Scanning Controversy
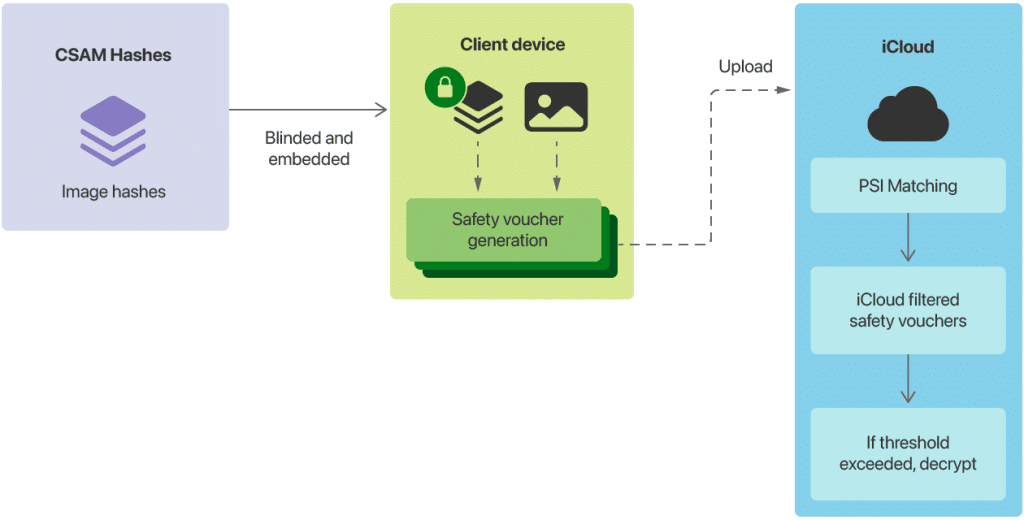
The announcement of Apple’s plan to implement CSAM scanning technology in iOS 15 sparked a significant debate about the balance between child safety and user privacy. Apple intended to use this technology to scan iCloud Photos for known CSAM hashes, aiming to curb the spread of child abuse material. While the initiative was rooted in protecting children, it raised concerns about the potential for surveillance and false positives, leading to a backlash from privacy advocates and some Apple users.
Following the public outcry and criticism from various stakeholders, Apple decided to delay the rollout of its CSAM scanning technology. This decision underscored the company’s willingness to listen to feedback and reassess its approach to implementing sensitive features. Although Apple emphasized the privacy-oriented design of the technology, the controversy highlighted the challenges of introducing measures that could be perceived as intrusive, even when intended for user safety.
Comparative Privacy: iOS vs. Android
When comparing privacy on iOS and Android platforms, several factors come into play. iOS’s closed-source nature and proprietary systems make it inherently more difficult for researchers to analyze apps for privacy violations. This opacity contrasts with the more open Android ecosystem, where apps and their behaviors are more accessible for scrutiny. Despite this, studies have shown that iOS apps may access sensitive data more frequently than their Android counterparts, suggesting that both platforms face significant privacy challenges.
Research indicates that the presence of tracking libraries, permissions usage, and personal information (PII) handling differ significantly between iOS and Android apps. While some studies have found a higher prevalence of potentially malicious libraries in Android apps, others highlight that iOS apps often access sensitive data more frequently, underlining the complexity of privacy issues across mobile operating systems. This comparative analysis reveals that, despite Apple’s rigorous privacy standards, there are still areas within the iOS ecosystem that warrant closer examination.
User Data Accessibility
Accessing personal data stored by tech companies has become a critical concern for users. Apple’s approach to data accessibility is notably more guarded than that of its peers like Facebook and Google, which offer straightforward processes for users to download their data. Apple requires users to navigate through multiple layers of its website to make a data request, a process that has been criticized for its lack of transparency and user-friendliness.
Despite these criticisms, Apple maintains that its stringent data access procedures are in place to protect user privacy. The company argues that by making data requests more deliberate, it reduces the risk of unauthorized access to sensitive information. This stance highlights the delicate balance between providing users with control over their data and ensuring that such control does not inadvertently compromise their privacy.
Advertising and User Profiling

Apple, while not as heavily reliant on advertising revenue as some of its competitors, does engage in targeted advertising within its ecosystem, including the App Store and News app. These ads are tailored based on user interests, which are inferred from their activities on Apple devices. By default, Apple devices allow the company to collect data to serve these targeted ads, though users have the option to limit this ad tracking. This practice raises questions about the balance between offering personalized experiences and respecting user privacy.
To mitigate concerns regarding ad targeting, Apple provides users with controls to limit the extent of their ad personalization. By navigating to the Privacy settings on their device, users can restrict ad tracking, thereby reducing the amount of personalized advertising they receive. This feature underscores Apple’s effort to provide a privacy-conscious advertising model, but the very presence of ad targeting within Apple’s ecosystem highlights the pervasive nature of advertising in digital platforms, even among companies that prioritize user privacy.
The Latest Privacy and Security Features
In 2023, Apple announced a suite of new privacy and security features, demonstrating its ongoing commitment to protecting user data. Among these features is NameDrop for secure AirDrop sharing and Live Voicemail, which transcribes voicemails in real-time, allowing users to screen calls without compromising their privacy. These features are designed with a privacy-first approach, ensuring that sensitive information is protected while enhancing the user experience on Apple devices.
The introduction of these features reflects Apple’s proactive stance on privacy and security, responding to evolving digital threats and user concerns. For example, the enhancements to Safari’s Private Browsing mode and improvements in photo privacy permission aim to give users even greater control over their personal information and how it’s shared. By continuously updating its privacy features, Apple reinforces its reputation as a leader in privacy innovation, striving to set higher standards for the industry.
The Global Surveillance Angle

Apple’s position on privacy also intersects with broader concerns about government surveillance. The company has been implicated in discussions about the PRISM program, through which the NSA is said to collect data from major tech companies. Although Apple, like other tech giants, has faced scrutiny over its potential involvement in such programs, the secretive nature of government surveillance makes it difficult to ascertain the full extent of any tech company’s participation. This ambiguity raises important questions about the balance between national security interests and individual privacy rights.
The challenges Apple faces in navigating government surveillance requests highlight the complex terrain of digital privacy. While the company asserts its commitment to user privacy, external pressures such as legal obligations and national security concerns can complicate this stance. This dilemma underscores the broader issue of how tech companies can protect user privacy in an era of increasing surveillance, emphasizing the need for clear legal frameworks and transparent practices that safeguard individual rights without compromising public safety.
Apple’s Privacy in Practice

Apple’s real-world application of its privacy policies is a critical measure of its effectiveness in protecting user data. Anecdotal evidence and case studies often reveal the practical implications of these policies, shedding light on how Apple’s privacy measures impact users on a daily basis. Whether through the handling of data access requests or the implementation of privacy features, the company’s actions speak volumes about its commitment to privacy.
Critically examining Apple’s privacy promises versus their realization offers insights into the challenges and successes of its privacy agenda. While Apple has made significant strides in enhancing user privacy, there remains a gap between ideal privacy practices and their practical application. This gap invites ongoing scrutiny and dialogue about how tech companies can better align their privacy commitments with user expectations and real-world needs, ensuring that privacy protection remains a dynamic and evolving pursuit.
Make Privacy Your Priority
Navigating the intricate landscape of digital privacy, Apple’s efforts stand as a testament to the importance of protecting user data. The company’s continuous innovations and adjustments in response to user feedback and evolving privacy challenges reflect a commitment to maintaining user trust in an era of increasing surveillance and data exploitation. As digital citizens, it’s imperative to stay informed and proactive about your privacy choices. Engaging with privacy settings, understanding the implications of new features, and voicing concerns are crucial steps in safeguarding your digital footprint.



