In an era where artificial intelligence (AI) is no longer just a futuristic concept but a present reality, its pervasive influence in various aspects of life is undeniable. However, this rapid integration of AI into daily life brings with it a host of potential risks that are often overlooked in the excitement of technological advancement. This article aims to shed light on the dangers of AI, delving into the ethical, economic, social, and security challenges posed by AI. It is a critical examination of the darker side of AI, highlighting why understanding and addressing these risks is imperative for a balanced future.
Contents
The Ethics of Artificial Intelligence

The ethical quandaries posed by AI are as profound as they are varied. When AI systems make decisions, such as in autonomous vehicles or healthcare diagnostics, they raise questions about moral responsibility and accountability. These AI decisions lack human empathy and understanding, potentially leading to outcomes that might be efficient but are ethically questionable. Furthermore, the programming behind these decisions often reflects the biases and perspectives of their creators, inadvertently perpetuating existing societal prejudices.
In the realm of privacy, AI’s capabilities transform into a double-edged sword. While AI can enhance security and personalized experiences, it also enables unprecedented levels of surveillance. This intrusion extends beyond government surveillance into the corporate sphere, where companies exploit AI for data mining, often without explicit consent. The resultant erosion of privacy rights poses a significant ethical dilemma, challenging traditional notions of personal space and autonomy in the digital age.
AI and Job Displacement
AI’s impact on the job market is a growing concern, with automation increasingly replacing human labor in sectors like manufacturing and the service industry. This shift promises efficiency and cost reduction for businesses but at the cost of widespread job displacement. The risk is particularly acute for routine, manual jobs, which are more susceptible to automation, potentially leading to significant unemployment challenges.
This displacement isn’t just a matter of lost jobs; it also widens the economic inequality gap. The benefits of AI-driven automation are disproportionately reaped by those who own the technology, exacerbating the wealth divide. Workers in affected industries face the daunting task of re-skilling in a rapidly changing job landscape, often without sufficient support. The long-term societal impact of this economic upheaval, if not addressed, could be profound, fueling discontent and social instability.
Manipulation Through AI

AI’s role in shaping public opinion and behavior through social media algorithms is increasingly alarming. These algorithms, designed to maximize engagement, create echo chambers that reinforce existing beliefs and viewpoints. This effect narrows the diversity of information individuals are exposed to, fostering polarization and undermining healthy public discourse. It also makes users vulnerable to manipulation, as they are less likely to encounter challenging or differing perspectives.
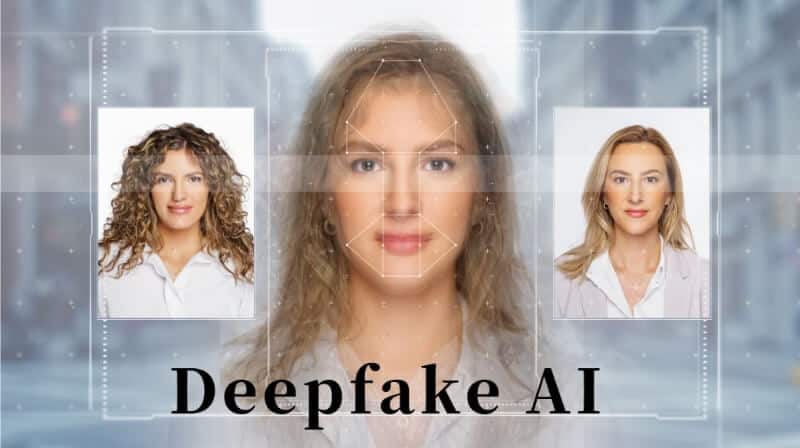
The use of AI in creating and spreading misinformation, including deep fakes, is another serious concern. Deepfakes, which are hyper-realistic fake videos or audio recordings, have the potential to disrupt the very notion of truth. They can be used to create convincing fake news, impersonate public figures, and manipulate elections or public opinion. The ease with which misinformation can now be created and disseminated poses a significant threat to the integrity of information, with far-reaching implications for democracy and societal trust.
AI and Cybersecurity Threats

AI’s integration into cybersecurity brings both advancements and new vulnerabilities. AI systems are increasingly used to identify and respond to cyber threats, offering faster and more efficient protection than ever before. However, these systems are not infallible; they can be exploited or manipulated, sometimes even turning the AI defenses into attack vectors. This evolving landscape creates a perpetual arms race between cybersecurity professionals and cybercriminals.
The threat extends beyond traditional hacking. AI-powered attacks are more sophisticated and capable of learning and adapting to bypass security measures. This adaptability makes AI a potent tool for cybercriminals, enabling them to carry out attacks with unprecedented scale and precision. From personal data breaches to large-scale disruptions of critical infrastructure, the potential for damage is immense. As AI continues to evolve, so too does the complexity of defending against its misuse in the cyber realm.
AI’s Role in Warfare

The utilization of AI in military applications heralds a new era in warfare, marked by the development of autonomous weapons systems. These systems, capable of making life-and-death decisions without human intervention, raise profound ethical questions. The lack of human judgment in these weapons can lead to unintended civilian casualties and escalate the potential for conflict, as decisions are made faster than humans can comprehend or control. Moreover, the prospect of an AI arms race among nations heightens global security concerns, potentially destabilizing international peace.
The risk of AI in warfare extends beyond autonomous weapons. AI’s capacity for surveillance and intelligence analysis can lead to more effective, but also more intrusive, military operations. This technology grants unprecedented power in gathering and interpreting vast amounts of data, which can be used in both defensive and offensive capacities. The dilemma lies in balancing the strategic advantages offered by AI in national defense with the ethical and safety concerns that its misuse could engender on a global scale.
Bias in AI Algorithms

AI systems are often perceived as neutral and objective, but in reality, they can reflect and amplify existing societal biases. These biases manifest in AI algorithms through the data they are trained on, which is often influenced by historical and societal prejudices. For example, AI used in law enforcement can perpetuate racial biases, leading to unfair profiling and targeting of specific groups. Similarly, AI algorithms in hiring processes might favor certain demographics over others based on historical hiring data that reflects past discriminatory practices.
The consequences of such biases are far-reaching and can reinforce systemic inequalities. In healthcare, biased AI algorithms can lead to misdiagnosis or inappropriate treatments for underrepresented groups. In financial services, they could result in unfair credit scoring and lending practices. Addressing these biases requires a concerted effort to ensure diversity in AI training data and ongoing monitoring and auditing of AI systems. The challenge lies in developing AI that is both technologically advanced and socially responsible.
AI and Mental Health

AI’s pervasive presence in daily life raises concerns about its impact on mental health and social skills. The increasing reliance on AI for social interaction through platforms like chatbots and virtual assistants may lead to a decline in human empathy and interpersonal skills. This shift can particularly affect younger generations, who are growing up in a world where digital interactions often replace face-to-face communication. The long-term psychological effects of this shift are yet to be fully understood, but early signs suggest a potential for increased feelings of isolation and a decrease in the quality of human relationships.
Additionally, the omnipresence of AI can lead to over-dependence and reduced self-reliance. The convenience of AI in making decisions and providing information can diminish individuals’ ability to think critically and solve problems independently. This over-reliance could potentially weaken cognitive abilities over time and increase anxiety when AI assistance is not available. The challenge is to find a balance between leveraging AI’s benefits and maintaining essential human skills and mental well-being.
Regulations and AI

The rapid advancement of AI technology has outpaced the development of regulatory frameworks governing its use. Current regulations are often inadequate to address the unique challenges posed by AI, from privacy concerns to ethical implications. The lack of comprehensive legislation leaves a gray area in terms of accountability and responsibility when things go wrong. This absence of clear guidelines hampers the ability to address the misuse of AI and protect citizens from potential harm.
There is a pressing need for international collaboration in developing AI regulations. AI technology transcends national borders, making it imperative for countries to work together to establish global standards and guidelines. These regulations should balance innovation and public safety, ensuring that AI develops in a way that benefits society as a whole. The involvement of various stakeholders, including governments, tech companies, ethicists, and the public, is crucial in creating a regulatory environment that fosters responsible AI development while safeguarding fundamental rights and values.
Shape The Future of AI, Your Voice Matters
As the world stands at the crossroads of AI’s expansive influence, this article has illuminated the multifaceted risks associated with its unbridled growth. The journey ahead requires vigilance and a collective effort to navigate these challenges. You are encouraged to engage in discussions about AI ethics, advocate for responsible AI development, and support policies that safeguard our societal values. Your voice and actions are pivotal in shaping an AI-integrated world that is safe, equitable, and beneficial for all.



